Haemodialysis
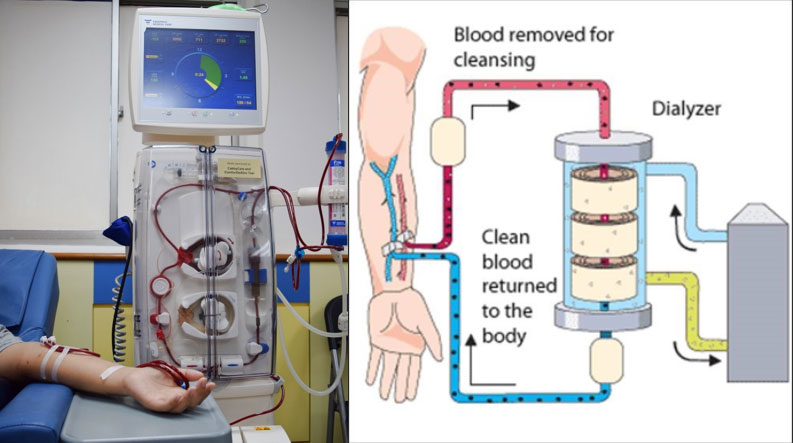
Haemodialysis is a process by which excess waste products and water are removed from the blood. This process requires an access to the patient's blood stream and the use of a haemodialysis machine. An access is a specially created vein in the arm known as the arterio-venous (AV) fistula.
During haemodialysis, blood is channeled through a plastic tubing (known as blood lines) to the dialyser which works as an artificial kidney (dialyzer). The dialyzer filters waste, removes extra fluid and balances electrolytes from blood to the dialysis solution (dialysate) and vice versa. The dialysate has a salt composition similar to blood but without any waste products.
Usually one dialysis session takes about 4 hours to complete and each patient requires dialysis 3 times a week.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Haemodialysis
Advantages
- Treatment is performed by nurses
- Three treatments per week at the dialysis centre; leaving four free days
- Social interaction with staff and fellow patients in the dialysis centre
Disadvantages
- Travelling to a dialysis centre
- Need to adhere to a fixed treatment schedule
- Spending four hours sitting on a dialysis chair during treatment
- Diet and fluid restrictions

